 There was a question on Twitter recently that asked what authors thought was the most important thing to think about when world building. The Tweeter listed a few considerations, amongst which was the word “culture”. I Tweeted a reply to point out that culture wasn’t a single thing. It was a number of related things. That exchange of Tweets led to this blog. Loosely termed, culture could be described as “the way things are done around here”. But that does oversimplify things a lot.  To think of culture as a single thing is like thinking of car just in terms of its exterior shape. It may look nice, but without an engine, gearbox, wheels, etc the car is nothing more than a pretty shape that serves no purpose. A working car is a “system” - and so is a culture. My training in cultural issues came while I was working for a living in business and at that time many businesses were struggling to change their cultures from old fashioned, top down, target driven, tightly controlled workplaces to places where the employees had greater input which, in turn, resulted in greater job satisfaction and hence to greater productivity. Such cultural change is not easy to bring about. Managers in those businesses often thought that such a change robbed them of their power and status, so they opposed it. They couldn’t do so openly, but they became experts at undermining change without revealing themselves. So, who would secretly oppose change in your fantasy world – and why?  Trades unions also opposed such change, but more openly, because they wanted a workplace that involved conflict as conflict formed their raison d’etre. A happy workplace is one where conflict is rare, so the unions have little part to play, so they don’t wield any power. Finally, the employees themselves feared change, because it brought uncertainty. This was especially true in businesses with a previously bad reputation for employee relations, because there was little or no trust in authority figures. A colleague of mine, with a PhD in organisational change, pointed out that “if you can’t change the people, you have to change the people”. In other words, there may be a few casualties along the way as the people who resist change are quietly shown the door to make room for people with more open minds. But that was business. What has that to do with “world building”?  It isn’t just fantasy authors who have to consider culture. All characters in all novels exist within a culture. Some of these are easy for us to relate to, because they are familiar, while others may not be. But if you get the culture right for your story, it will make your character’s conflicts easier to understand. This is especially so if they are taken out of their own, comfortable culture and placed in one where they feel like an alien. Just going to a different town can make some people feel like that, so imagine what it feels like for someone going to a country on the far side of the world - or the far side of the galaxy. Understanding the elements that make up a culture allows the world builder to build something that is believable. The granddaddy of fantasy, Tolkien, got this right (mainly) with his Lord of the Rings trilogy and authors who have modelled themselves on Tolkien’s style tend to get the culture of their worlds right as well.  Experts on culture talk about the “cultural web”. These are the interconnected elements that make up the organisation’s culture. If you are worried about my use of the word “organisation” please don’t be. I’m not using it in the business sense. Any society is also an organisation and the world you build is just another society, supported by its own cultural web. The stronger it’s cultural web, the stronger the society that comes out of it. One of the reasons that revolutions fail is that they sweep away an old, outdated culture, but neglect to put the right elements into place to support the culture they want for the future. This leaves a vacuum into which counter revolutionaries can slip to undermine the new regime. Your fantasy world is just another form of country, with its pro and anti-revolutionary elements. If your hero wants to bring down an evil empire, they need something with which to replace it, or the old regime will simply return in a new disguise – just as Sauron was able to return in LOTR. Think about Putin and Russia in 2023, compared to the old USSR which everyone thought had been swept away in 1991. The similarities are many even though it isn’t now a communist state. But it isn’t a democracy either. The leadership and political ideology may have changed, but the underlying culture didn’t. So, what makes up the cultural web? Well, the graphic below lays it out in visual form, but I’ll take you through the various elements.  At the centre is the “paradigm”. This is the set of ideas or concepts that make up the world that you are building. Some of these are mutually exclusive. You can’t have a world ruled by a King that is also a Republic, for example. This is where your antagonist becomes very important. Whoever is running the Evil Empire has to have some reason for doing it. They must also have some idea about what they want achieve from what they are doing. This is where LOTR actually fails, for me. I can’t understand what satisfaction Sauron gest from all that power. Just desiring power is too shallow for me. Power needs a purpose, otherwise it is of no use. So, to start your world building you have to construct a paradigm for it. That is all about the ideas and beliefs that underpin whatever its happening. What does “Evil” want to achieve and what does “Good” want to put in the place of Evil. Those things will define how the people live. If it is a tyranny, then you can’t give the people any power when it comes to decision making. On the other hand, if it is a collective, then the people will have plenty of say in what happens. Those are two extremes, of course.  Surrounding the paradigm are the six inter-connected elements that make the paradigm work. Leave out one, or put the wrong things into it, and the paradigm itself won’t stand up to scrutiny. For example, if you have a tyrant that controls the lives of everyone, you can’t also have an independent legal system, because that would be able to say “no, you can’t do that” to the tyrant. Sauron didn’t have a Court of Appeal, for example. Instead he had Ring Wraiths and Nazgul. So, the most important bit of the cultural web, after the paradigm, is the organisational structure that supports it. Traditionally there are three parts: The lawmakers (tyrants, kings, nobility, politicians, etc). Then there are the people responsible for applying the law (Civil servants, administrators, local government, police, Ring Wraiths etc) and finally there is the legal system that sorts out the disputes over what the laws really mean and how fairly they are applied. Even if you have a tyrant running your world, you’ll still have a legal system – it just won’t be a very fair one. For example, the legal system may just be made up of “enforcers” who go around imprisoning, or even executing, anyone who criticises the ruler.  Next up are the power structures. Now, you may think that I’ve already covered those above, but not everyone who wields power is part of the organisational structure. Other people hold power of one sort or another. Businesses, trades unions, religions and more. Who you give power to in your world is quite important as those people can be enemies or allies, whichever you choose them to be. And the amount of power they wield can have a serious impact on your plot. An ally who is powerless isn’t of much use to you and an enemy without a source of power is easy to beat. Your magical figures will fit under this heading, because magic is a source of considerable power. Control systems are a bit abstract in many ways. If you are a King and you make a law, how do you make sure that the people obey that law? There has to be some way to do that. The most obvious example is the police and legal system, but there are other ways of exercising control. Fear is one (don’t stand on a balcony in Russia), wealth is another – either as a reward or a penalty. Control of other resources is a source of power, so it's another way of ensuring compliance.  So, how does your tyrant make sure the people obey? And if you want to depose the tyrant, what control systems must you dismantle or subvert? The whole point about the One Ring was that it was able to control the beings that wore all the other rings. It was even engraved on the inside of it, so everyone knew what it was! And if you dismantle the existing control system, by destroying the One Ring for example, how do you then exercise control afterwards? Or do you let your world descend into anarchy?  Rituals and routines form an important part in maintaining control over people. Getting people into church (or a mosque or a temple) every week, for example, prevents adherents to the religion from drifting away. The more people you have in your religion, the more power you wield, so you don’t want to lose any. It is also where messages can be sent out and heard. Historically, the pulpit has always been used by governments to send out its messages and to exercise control. I’m sure we can all think of countries where this still happens. But those aren’t the only rituals. Weddings, funerals, christenings, workplace meetings, even getting together once a week for a family meal, to watch TV or go to a football match, all form part of the rituals that identify us as being part of a community. Taking part in a ritual says “I belong here.” They also say “I am conforming, so you don’t have to send me to prison or execute me.” They can be used for good as well as evil.  Believe it or not, stories play a very important part in culture. Stories about heroes encourage the sort of behaviour you want to support, while stories about villains tell you what sort of behaviour you want to discourage. It’s why Bible stories are told, it’s why Aesop wrote his fables and it’s the way the media influences public onion on a wide range of issues. (and you thought they just reported the news) But the heroes and villains of these stories will be different in every culture. In a communist country the heroes might be Marx and Lenin. In Britain Robin Hood is a hero, which is no mean achievement for a thief. Marvel and DC comic books are all about telling stories that express American values. Cults create heroes out of ordinary people, often stretching the truth or telling lies to make the person seem more significant than they were. The media often creates heroes – and villains. Sometimes they even start as heroes and then get turned into villains when the media wants to change the narrative. You will be familiar with the old saying that one man’s terrorist is another man’s freedom fighter (Nelson Mandela). And one man’s despot is another man’s saviour of the nation – politics tells us that because we all see politicians as one or the other depending on which side of the fence we are viewing from. It’s the stories that are told about them that make them one or the other.  Finally, we have the symbols of our culture. Many of these are physical, such as flags, buildings, coats of arms, etc. We have symbols of wealth that encourage people to strive to achieve. Religions are very big on symbols, as they are with rituals. We salute the symbols we support and we tear down those we despise. But there are also more abstract symbols with which we engage. Symbols may take the form of songs (national anthems are a symbol), the sports we play or watch, etc. The language we use is a symbol, as are phrases such as “motherhood and apple pie” because they are symbolic of cultural values. If you wear any sort of badge (including wrist bands etc) or you wear a tee-shirt with a slogan on it, you are wearing a symbol that declares your allegiance or an ideal you support. The same will apply to your characters. I'm sure that we can all think of symbols that have played a powerful part in events. A swastika will forever be a symbol of hate. So, a lot to think about if you are a world builder who wants to create a world that is believable. I have used mainly real world examples to illustrate what I mean, so if you are a fantasy author you will have to imagine the equivalents for your world. But with a strong culture that your readers can identify, the hero will be able to do things to change the culture for the better and the villains will oppose those changes, which makes for a more satisfying plot. Your hero may spend a lot of time killing dragons, but what do they do with the dragon’s horde once the dragoon is dead? If they keep it for themselves, they are just as bad as the dragon (Thorin Oakenshield in The Hobbit), so they must use it to either support or change the paradigm you created for their world. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so.
0 Comments
 Never judge a book by it's cover. Every picture tells a story. Which of those two old sayings resonates most with you? For us it's the second, because book covers are supposed to tell a story and there is no doubt that readers make judgements about them. So what story is your book covers telling? When readers do searches for books, or even when they are just browsing through the listings, what is the first thing they see? It is one of two things – either a book’s title or its cover. Sometimes it’s both because the title is on the cover anyway. I’m not going to talk about titles. There are too many theories about what makes a good title and, so far as we can tell, one theory is as good as another. Here’s one we found, but there are hundreds more. But the same can’t be said for covers. They have to convey so much information in a simple image and, sometimes, it’s easy for them to convey the wrong information.  Take the book on the right which was, until recently, the cover for the first book in our Magi series. We had thought it was quite a good cover, which is why we stuck with it when we signed the author. That was until we got a bit of feedback that told us we were way off track with it. Someone had emailed us asking if we would be prepared to provide a few paperback copies of one of our books for discussion by their book club. They were raising money for charity through a small attendance fee and income from tea and cake sales and, once the books had been read, they would be sold second hand, also to raise money for charity.  Happy to make our contribution, we happened to have a few spare copies of The Magi lying around the office, so I emailed her a synopsis and the cover image. We were quite taken aback when the lady replied “We are a church group and aren’t in the least bit interested in a book about BDSM. Thanks for the offer but we’ll go elsewhere.” (If you are an innocent type who is unfamiliar with the term BDSM, we don’t suggest you Google it). We were puzzled by this response, so we emailed back asking what she meant, to which she replied that with the leather clad lady on the cover, it was clearly a book of an erotic nature and that BDSM was implied.  We emailed back to assure her that the book had no erotic content at all (sorry if you are disappointed by that) and peace was restored, but the book still wasn’t accepted because, with that cover, they didn’t want to sell it on their second-hand book stall. But we had learnt a valuable lesson. The cover was designed by a previous publisher, with whom we are acquainted, and I feel certain that he had no intention of implying that the book had anything to do with BDSM. But, looking at it in light of that response from the book club, I could now see what the lady was getting at. And the image of the leather clad woman appeared on the cover of all 9 books in the series, and on the box set. It was part of the “branding” of the series.  Then there are the other two elements used on the covers. The inclusion of the image of a distant galaxy is appropriate as it’s a sci-fi book. That was also part of the series branding. The third element, however, in this case an “electronic egg” changed with each book in the series, to tie in with the plot of the book. With doubt now weighing us down, we started to wonder about that suitability of that egg image, too. What did it suggest to the readers?  So, we asked a few of our readers for their opinions. The general consensus was that it was confusing. How could you have an electronic egg? What would an electronic egg do? Why was the egg floating in space? Was it some sort of spaceship? What had the egg to do with the woman? Was that the way babies were born in the book? Well, if the cover was causing as many questions as that, it clearly wasn’t doing its job of selling the book. As it happens, the answers to the questions are contained within the book but, of course, no one was going to buy the book to find that out if they were confused about it in the first place. One thing we know is that readers don’t like to be confused before they even read the first page. In fact, it’s only the readers of crime fiction (and not all of them) that are willing to be confused by their books.  So, we decided that (a) the book’s image sent out the wrong message to some people and (b) it confused other people. Which was, perhaps, why the book and the series hadn't been doing as well as it deserved. It is rather good, as many sci-fi readers have discovered (but you would expect us to say that). So, we set out to create 9 new book covers that presented a less confusing message. In fact, all we wanted the images to say was “this is a sci-fi book”. One or two of them do hint at the content, the ones for “Cloning Around” (Book 4) and “Timeslip” (Book 5 – image to the left), but the others are a little bit more generic.  If they say anything it’s “This is sci-fi and weird stuff will happen”. (BTW, you can find out more about the books shown on our "Books" page or by clicking on the images) So, what does your cover say about your book? Does it give out an unintentional message, the way ours sent out a BDSM message? Does it confuse the reader? Is it different enough to make it stand out from the crowd? Because that third question is also important. When readers do a search by genre, they get presented with list after list of books, which they then scroll through. The cover of your book has to stand out from the crowd if you want the reader to click on it and find out more. If the cover looks too similar to the ones above and below it, the reader’s eyes are going to slide right past. Yes, do be bold, be different; but make sure that the key message about your book is plainly understood from its cover image. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so.  Big businesses spend a lot of money on advertising. I think we all know that. They spend it because it works, otherwise they wouldn’t do it. One of the reasons they spend so much on advertising is because they keep launching new advertising campaigns. They will run a campaign for a few weeks or maybe a few months, then they’ll stop for a while. Then they’ll start a brand new campaign with different ads. The ads may be similar, using the same characters or the same voices, but they will look different. The characters will be in a new setting, or the voices will be fronted by new images. But it’s the same product that is being advertised. So why go to the expense of re-making ads so often? Why not just continue using the same campaign all the time?  It’s because we, the public, get used to seeing an ad, so after a while we don’t pay it any attention. We need something fresh to make us watch the ad and hear the message once more. It’s a bit like teenagers being told to tidy their rooms by their parents. If you thought that your teenager isn’t listening anymore, you are probably right. They’ve heard it so many times, they’ve “tuned out” the message. And we all do it. Which is why advertisers spend so much money trying to attract our attention again by making new adverts. So, what has this got to do with Indie authors? you may ask. I’m so glad you did. "But that will stop working after a few weeks." Indie authors spend a lot of their time using social media to promote their books. It’s free unless you use the paid advertising facilities. The most common way to use it to promote work is to post a bit of blurb and a link to where the reader can find out more. The link then pulls the cover image through from the retail site so it can be seen on the social media site. That’s fine if you don’t want to pay for advertising. But that will stop working after a few weeks. Like adverts for big businesses, people will soon “tune out” your advert because once they’ve seen the cover, it is too familiar to bother with. They either bought the book several weeks ago, in which case they aren’t going to buy it again, or they are going to scroll past it. So, the indie author has to do what the big businesses do. They have to “refresh” the message. How can you, as an indie author, do that? Well, the image is the first thing to look at. Are you relying on the link in the post to reproduce the book’s cover from the sales page on Amazon, or another retailing site? If you are, then you can’t change the image unless you change the actual cover. But, actually, you can.  You can upload a new image into your Facebook, Twitter, Insta, etc post. That way it will take priority over the link to the sales page and will be the image that is seen. The link is still there for people to click on, but the image you use can be changed in multiple ways to keep the message fresh. It also has the advantage that you can be more creative with the image and do things that a simple link to Amazon (or whatever) can never do. You can create 3D images of your book’s cover.  You can overlay the 3D image onto an atmospheric background, along with some text. If the book is part of a series, you can show two or three covers side by side in a single image. You can change the orientation of the image to make it more suitable for viewing on a phone or tablet. Ultimately, you can create a “trailer” for your book, using video imagery alongside your book’s cover. That is really eye catching. By now, some of you will be asking “How can I, an impoverished author, create those sorts of images?” Well, if you can use PowerPoint you can do some of that. You can even make videos if you download free apps like “Moviemaker”, which can join together images created in PowerPoint, accompanied by a narration, text or music. If you want to invest in some software to help you, there is Photoshop, Canva and one we reviewed a couple of weeks ago, called Book Brush, which specialises in creating those sorts of images for authors. There are probably other packages available, but we’re not going to list them all. Will it cost much? Well, somewhere between £100 - £200 ($110 - $220) will probably cover it.  Immediately some of you will be saying “I can’t afford that.” To which I will reply “Can you afford not to sell any books?” If your books aren’t selling, then doing nothing is not an option. Einstein defined insanity as doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different results each time. I’ll put it a slightly different way: If you always do what you always did, you’ll always get what you always got. If you want a different outcome, you have to do something different. That applies to life in general, of course, but this isn’t a philosophical blog. Just be assured that if your books aren’t selling using whatever methods you are using now, they will continue not to sell unless you change your methods. And what you do has to be within both your ability and your control. Unless you want to contract an expensive marketing agency to promote your book, you have to do whatever it is within your power to do. "I know you don’t want to hear this but, by itself, using social media for free is never going to turn anyone into a successful indie author." One of the ways you can do that is to change your post’s images and messages at regular intervals. And to do that you need the right tools. I will admit that there is an element of risk involved here. You may spend money on buying an app to help you create more or better images and you may not increase your book’s sales at the end of it. But, on the upside, if it works and you sell more books, your investment will repay you, because you can use those apps time and again to create more and more new images. But rest assured, if you don’t spend the money, nothing will happen anyway. Success doesn’t come for free, as any indie author who is selling a lot of books will tell you. We are selling quite a lot of books because we are spending money. We aren’t a big business so we can’t afford to spend much. But if we didn’t spend anything, we wouldn’t sell enough books to cover our day-to-day running costs. I know you don’t want to hear this but, by itself, using social media for free is never going to turn anyone into a successful indie author. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so. Disclaimer: We are not connected with Kindlepreneur in any way and have no financial interest in the product reviewed in this blog. This review has not been paid for by Kindlepreneur, Dave Chesson, or anyone else.  Not the real product's logo! Not the real product's logo! Let me make it clear up front, if you only have one book published and never intend publishing another, you aren’t doing much marketing and you don’t intend paying for marketing, this product may not be of much use to you. But if you intend having a lengthy career as a self-published author, if you are planning to publish a series, or if you are a small, independent publishing house like us, then there is probably something here to interest you. Warning: This is a lengthy blog because for authors and publishers to understand the value of the product we are reviewing, they also have to understand the need for it. What need do you have that this product satisfies? You may not even know you have that need until you read this blog. Publisher Rocket is an aid to marketing and an aid to advertising using Amazon Ads and other advertising platforms. One of the things every publisher (I include self-published authors in that) has to know is which keywords to include in their book’s description in order for it to attract the attention of readers when they are looking for something new to read.  If you have ever uploaded a book onto KDP, you will know that you are allowed to enter 7 “keywords” into your book’s details. Actually, you can use more than 7 words, because you can enter “strings” of words. For example, you don’t have to limit yourself to “romance” as a keyword, you can enter “modern romance” instead and it will still only count as one keyword. When readers are searching for books to read they may use Google, other search engines, or the search bars of retail sites such as Amazon. Very often they don’t know exactly what they are looking for, so they can’t enter a title or an author’s name. Instead, they enter a word or string of words that describes (for them) the type of book they want. For example, as a fan of historical fiction, I may do a search using those two words. Or I might add “military” to the description because I like historical fiction set around military themes. Or I might use “World War II” as my search term. "they are wasting one of the 7 keywords that KDP allows them." If the author knows what search words the readers are using, they can make sure those words are included in their 7 keywords for their book’s description on KDP, so they are guaranteed to be found when a search is done, and the book will appear in the search results - though not necessarily near the top of the list. But authors also need to know which words not to include; the words that readers rarely use for searches. If the author uses them, then they are wasting one of the 7 keywords that KDP allows them.  The problem is, identifying which words the readers are using. It may not be the ones we think they are. You may think I’m talking about “Search Engine Optimisation” (SEO) and you are dead right – I am. Only we don’t need to use a fancy term like that, and we certainly don’t need to pay someone to do that for us. Manual targeting on Amazon Ads is the most cost efficient way of using that advertising platform. But it relies heavily on the advertiser (you) knowing how to get the best out it.  So many genres - but which one is the best fit for your book? So many genres - but which one is the best fit for your book? The first type of manual targeting uses your book’s genre. Anyone who buys books in the same genre will have your book in their “recommendations”. Amazon Ads suggests the genres and you can delete any that you don’t think really apply. For example, Amazon Ads may suggest both modern and historical romance for your book, but your book can’t be both, so you can delete the one that doesn’t apply. But you can also insert your own genres. For example, if yours is a fantasy book with a strong romantic sub-plot, you don’t have to limit your advertising to the fantasy genre. You can add romance genres too. Do you know which genre listing on Amazon is going to be the best for your book? Some are better than others for getting your book seen and, according to Publishing Rocket’s publicity video, there are “hidden” genres too. For some genres you can even get to the number 1 bestseller spot by selling only a handful of copies. That is useful stuff to know – but how do you find out which genre(s) you should be advertising to? Read on to find out. By the way, did you know that you aren’t limited to just 2 genres on KDP? That only applies when you first upload your book. Once it is published, you can select up to 7. You need an account on Author Central and then you need to go to Help>Contact>Amazon Store & Detail Page>Contact us>Amazon Book Page>Update Amazon Categories.  The second type of manual targeting uses keywords. Amazon Ads tutorials suggest using between 100 and 150 keywords (or keywords strings) in an ad such as this. If you struggled to come up with 7 keywords for your book, how are you going to come up with 100-150? Well, using author names and the titles of similar books is one way. But whose books and which titles? Which is where Publisher Rocket comes in. OK, it took a long time to get here, but if you don’t understand the basics of Amazon (or other platform) advertising, you aren’t going to understand the value of this product. What Publisher Rocket does is gather together the search terms that are used on Amazon and presents them to you for your consideration. But it also does much more than that. It also provides data which tells you which of those terms is best at turning advert “clicks” into sales. "Publisher Rocket helps to sort the wheat from the chaff"  Not all search words are equal, you see. Sometimes the reader enters fairly random words into the search bar and therefore the results they get back don’t provide them with what they are looking for, so they have to have another go. But if the reader clicks on a book out of curiosity, those random search words still appear as results, so it is essential to know that they aren’t that useful, so as to exclude them. Publisher Rocket helps to sort the wheat from the chaff by providing the user with a wide range of data that they can download into a spreadsheet to filter and sort to their heart’s content to answer the vital keyword questions they may have. The one thing they don’t want to do is pay for clicks on their ad which won’t be converted into sales. Just because they and Isaac Asimov both write sci-fi, it doesn’t mean that their readers and Isaac Asimov’s readers like the same sort of books. They may want to exclude that name as a keyword for that reason, so that they don’t pay for clicks from curious Isaac Asimov readers who aren’t going to buy their books.  OK, if that sounds complicated, that may be something for just the real data nerds to get into. For the rest of us, Publisher Rocket provides us with some simpler tools to use to find words that are good to use for our books, by genre, and what aren’t so good. Using the app is easy enough, but Publisher Rocket’s owners make it even easier by providing “how to” webinars to guide you through the various functions and offer advice on how to get the best results. The owner of Publisher Rocket is a company called Kindlepreneur, a company created by self-made Kindle millionaire Dave Chesson. This isn’t their only product, but it is the one we have found to be most useful in helping us to increase the efficiency of our advertising campaigns. If you saw our blog last week (see below the end of this blog), you will know that this is something we have been focusing on in recent months and it has paid off for us. Publisher Rocket costs $97 (around £85) for a lifetime subscription, which is why it may not be suitable for people who only ever plan to publish one book and who don’t intend getting into marketing. In other words, it isn’t any use to an author who doesn’t want their book to be read. Those that do want their books to be read may find it more useful. "As a publisher this was a no brainer for us" But even if you only have one book, the purchase price could be paid back quite quickly (it is the equivalent to approximately 50 extra sales) if you use the results to improve your advertising efficiency. As a publisher this was a no brainer for us. We bought Publisher Rocket in November last year and it had paid for itself by Christmas. We don’t use it every day, but when we do use it we know we are going to get the most bangs for our buck out of our advertising. So, if you need some help with your Amazon Ads, this product may be just the thing and we are happy to recommend it. If you want to know more about the product, click here. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so. Disclaimer: We are not connected with Bryan Cohen in any way and have no financial interest in his book. This review has not been paid for by Bryan Cohen or anyone else.  This book probably represents the best £3.99 I have ever spent since I started publishing. That is because it’s a book that actually paid for itself several times over. I would go so far as to say I wish I had read it 5 years ago, as it would have saved me a lot of time and money. That isn’t actually possible, as the book was only published this year, but you know what I mean. This article will be half book review and half blog. The blog part tells you what happened when we tried to apply the ideas and methods that Bryan Cohen recommends in “Self-Publishing With Amazon Ads”. Some of you may just want to know how that worked out, so that bit is at the end of the article. "You’ll have to find out the hard way that there is no such thing as “instant gratification” when it comes to marketing a book." If you are still reading this now, and haven’t scrolled down to find out what happened, you have one of the key qualities that Bryan Cohen talks about in the book: patience. Cohen doesn’t promise instant results. One of the first things you will learn from this book is that generating consistent results from Amazon advertising is a marathon not a sprint, and if you aren’t prepared to be patient then this may not be the book for you. You’ll have to find out the hard way that there is no such thing as “instant gratification” when it comes to marketing a book. If you have never used Amazon Ads, or you have only just dipped your toe in the water, then you will be at a bit of a disadvantage, as Cohen assumes some prior knowledge. But don’t worry. That prior knowledge is available. Amazon Ads provides webinars for its new users here. "helping authors to reduce the amount of money they spend while also getting better results" A word of caution about the webinar. It is aimed at encouraging you to spend money with Amazon Ads. After all, Amazon Ads is a business and it makes its profits from its users, so the more money users spend with them, the more profit Amazon makes. Bryan Cohen’s book, however, is aimed at helping authors to reduce the amount of money they spend while also getting better results. This means that some of Cohen’s advice on bidding strategies contradicts that of the webinar. And if you are wondering what a bidding strategy is, it means that you need to do the webinar before you dive into this book. Just a quick word about the author. He is a self-published author himself and he also provides self-publishing training and other services for authors through his website Best Page Forward. But not all the training he provides has to be paid for. Each quarter he hosts the 5 Day Amazon Ads Profit Challenge, which is free to join and which has provided coaching for over 25,000 authors. "She challenges Cohen at every turn" Each chapter in the book takes the reader through a different phase of a process that starts with poorly performing ads and progresses to turning those ads into high performing ones. Each chapter therefore introduces a new idea or method, so if you try to skip ahead to the “good bit”, where you are making millions, you are likely to miss out on a vital step which means your objective won’t be realised. See, once again you have to be patient. Just something to note. Early in the book Cohen talks about creating 5-10 ads a week. This is for the benefit of American readers, because Amazon.com allows readers to create customised ads and advertisers are encouraged to create several different customised ads a week to appeal to different segments of the market. That facility doesn’t exist for users of other Amazon markets (yet). For us, the Amazon page for our book is our ad. That is actually a timesaver for us, because one ad can run forever. However, the rest of what Bryan talks about is completely valid and if we ever get access to the customisation function, we'll be ready for it because we've read this book. Each chapter is broken down into two parts. One part is a “fly-on-the-wall” view of an on-line coaching session with one of Bryan’s clients, a woman called Erin. The other part is Bryan speaking directly to the reader to explain what he is teaching Erin. I don’t know if Erin is a real person or a composite character created for the reader’s benefit, but she is the person who asks the questions that the reader might want to ask. She comes to the course as a sceptic and has to be shown that the process works by actually implementing the methods herself so that she can see the profits from her ads increasing over time. And Erin isn’t a passive student. She challenges Cohen at every turn, especially on the issue of how long it will take to see returns and how she is going to fit in the time to do what he recommends. Because, as with all things, time is one of the most valuable resources we have and, as writers, we’d rather be spending our time writing than marketing. But Cohen is ahead of Erin here as well and there are specific sections on time management. "only a handful of people will ever achieve 6 digit profits" One of the things I liked about the book is that it is grounded in realism. When Cohen talks about increasing royalties and profits (not the same thing, as you will find out if you buy the book), he doesn’t promise telephone number sized amounts of money. He talks about investing $50 dollar a month to make $100 profit, which gives a feeling of being achievable. He then talks about increasing that profit to $200, $500 and maybe $1,000. He does refer to people who have made considerably more, but he tempers that with the realism that maybe only a handful of people will ever achieve 6 digit profits – but you get a warm feeling from knowing that, by doing a bit of work, you could be in that handful. Cohen is just as realistic about how much time we have available to do the work. He knows we have day jobs, families to look after and writing careers to pursue, so he tries to optimise the amount of work we may have to do in order to make best use of the time we have available. Time management is a key message. Readers of this blog will notice that I have only given the book 4 stars and therefore I had some reservations about it. That is true, but the reservations aren’t about the lessons that Cohen teaches, they are more about the way they are presented. For a start, Cohen refers to some calculations you may want to do in order to produce some performance data. Some worked examples would be very helpful to understand what he is talking about, but they are lacking. "bombarded with a whole lot of data" There are no handy graphics, such as screen shots of Amazon Ads pages, where things can be pointed out. While I am quite good with the internet, there are features I miss on web pages and some key features aren’t always the most prominently displayed. A graphic pointing out “This is the button you need to click” and “This is where you have to alter x” would be really helpful. The other thing I had a problem with is the additional applications that you might want to use, especially those relating to generating lists of keywords (If you don’t know what a keyword is, then see above regarding the Amazon Ads webinar). One of the applications has to be purchased (about £100) and comes with its own training videos, so that’s OK (it isn’t essential and you don’t have to buy it, but it is a useful tool and we will review it next week). But the other two are plug ins for Google Chrome, which are free and come with neither a user guide nor helpful training videos. I tried using them and was bombarded with a whole lot of data which I struggled to interpret. Some guidance on how to interpret the data produced by those plug-ins (with accompanying graphics), so that I could use it in ads, would have been really useful. But don’t let those three things put you off buying this book. Firstly, with a bit of patience (again) I found the buttons I needed to click and the things I needed to adjust. And, with some trial and error, I did work out how to interpret the data produced by the plug-ins. But it took time that I hadn’t factored in and which I had to divert from other activities. "while we were doing a lot of things right, we were also doing quite a few things wrong" So, how did we get on? The first thing you need to know is that here at Selfishgenie we aren’t complete novices. We have been running Amazon Ads for many years, with mixed results. From articles I had read on various websites I found out that advertising with Amazon wasn’t a quick fix. We would need to spend more money than we had in the past and let our ads run for longer if we wanted them to be successful. So, around April 2022 (before we bought this book) we decided to commit some of our sales revenue to improving our advertising, as an investment to make more revenue in the future. And it worked. We launched an ad campaign for our Carter’s Commandos series and saw our monthly royalties increase from the low three digit level per month to a four digit level by October, which we were able to maintain. But the amount of money we were spending to get that revenue seemed to be higher than it needed to be. In terms of profit on the campaign (the net amount we made from each sale compared to the gross amount we spent), we felt sure we should be doing better. That was when I stumbled across Bryan Cohen’s book. Actually, I did a search looking for blogs about using Amazon Ads and it appeared in the search results. It didn’t take long to discover that while we were doing a lot of things right, we were also doing quite a few things wrong. In particular, our bidding strategy was wrong. We thought we could buy sales by spending more money. In fact, all we were doing was giving Amazon more money than we needed to, which was reducing the profit from the sales we did make. "give away Bryan’s secrets for free" The way Amazon’s advertising algorithms work mean that bid price is only one factor in getting our ads seen. I won’t steal Bryan Cohen’s thunder (or reduce his books sales) by telling you what the other variables in the algorithms are. (I know, but it wouldn’t be fair to give away Bryan’s secrets for free). I won’t bore you with all the details of what we did. Suffice to say that we learnt the lessons that Bryan Cohen was trying to teach us.  But what we did do was to run a trial to see how his methods compared to our own. We continued to advertise our Carter’s Commandos series the way we always had. But our Magi sci-fi series had been bumping along the bottom, making very few sales per month. So, we started a brand new ad campaign for the first book in that series and applied the newly learnt lessons to that series to see what happened. NB. When I refer to "sales" below I also mean KindleUnlimited (KENP) pages read. 1st 30 Days The good news is that we got clicks on our ads from Day 1 and we made more sales than in the previous 3 months, but they weren’t Earth shatteringly good. The campaign wasn’t profitable, meaning we spent more than we received in Royalties. We tweaked the book’s blurb (see last week’s review of “Fiction Blurbs: The Best Page Forward Way”), but there wasn’t much else we could do to stimulate more sales during that period. 2nd 30 Days Here we started to reap the benefit of “delayed results”. It is said that buyers have to see an ad an average of 7 times before they respond. This seemed to be the case as the number of clicks on our ads increased the longer the ad ran and we started to see more sales. But we also started to see sales for books we hadn’t advertised. The Magi is a 9 book series, and we were only advertising Book 1. But we started to get sales for books 2 – 9, which we hadn’t advertised. Our original ad was instrumental in developing a “fan base” for the series. These additional sales meant we were now in profit. Final 30 days I’d be lying if I told you that sales really started to take off. But they did continue even if they were unspectacular. There seems to be some sales resistance to The Magi series which we aren’t getting for other series, and we need to dig into that to see if we can work out what is causing it. The final 30 days of the trial was also during January, when money is traditionally tight for people - even avid readers of sci-fi. However, we have sold more copies of titles in The Magi series in the last 90 days than we did in the previous 9 months and the campaign is showing a profit, so overall we count it as a success. "highly recommended" So, what are the main take-aways we have from the book? 1. This isn’t a quick fix. We required patience and strong nerves to spend money without seeing a profit for several weeks. 2. If we are doing a “category ad” (advertising by genre), we needed to keep the band narrow so as not to waste money on genres that aren’t relevant and where our ad may generate a click (which we pay for) but won’t get converted into a sale. 3. We needed to use more keywords in our ads and we had to make them relevant to the genre of books we were selling. The Magi series is “space opera”, so there is no point in using keywords that relate to dystopian sci-fi. Again, they may generate clicks, but they won’t get converted into sales. 4. We needed to use the data from the ad campaigns to help reduce our costs. For example, we were getting hundreds of clicks for one keyword, generating cost, but the clicks didn’t convert to sales. Conclusion: readers who use that keyword aren’t interested in our book. So, we deleted the keyword from the list. 5. It works!  Having learnt from this experience, we have now tweaked our ad for Carter's Commandos, to take into account what we now know we can do better, which hasn't increased our sales but has reduced our costs, so we are actually keeping more of our money, which is a win, which makes us happy. If you are an Indie author or a small publisher (like us) then “Self-Publishing With Amazon Ads” by Bryan Cohen is highly recommended. To find out more about the book, just click or tap on the cover image at the top of the blog. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so. Disclaimer: We are not connected with Bryan Cohen in any way and have no financial interest in his book. This review has not been paid for by Bryan Cohen or anyone else.  This is a review of one of two books by Bryan Cohen that we think should be read in the right order. This first one, “Fiction Blurbs: The Best Page Forward Way” is about improving your blurb writing technique so that readers feel more compelled to buy your book. The second book, “Self-Publishing With Amazon Ads” teaches you about increasing the profitability of your advertising campaigns. What links the two? One of the “tweaks” that the second book suggests to increase sales is to improve your book’s blurb. So, if that is a tip for increasing sales it seems sensible to us to try to improve our blurbs before we started spending money on advertising, so that we don’t spend money on advertising only to find out that our blurbs might need improving.  Still not quite right! Still not quite right! It is putting the metaphorical horse in front of the cart rather than behind it. But don’t worry, we’ll be reviewing “Self-Publishing With Amazon Ads” next week, so that you can get the whole picture. Having said this book is by Bryan Cohen I must now correct myself and tell you that it is actually written by Phoebe J Ravencraft, an associate of Bryan Cohen, who works for his company, Best Page Forward. But they get joint author credits. First of all, what about the authors’ credentials for writing a book such as this? Best Page Forward has written over 5,000 book blurbs for self-published authors. Phoebe herself has written or overseen the writing of around 3,000 of those. She comes from an advertising copywriting background. They have gathered plaudits from satisfied customers and the blurbs they have created have stood the test of time to sell books. I think we can safely say that they know what they are talking about.  In one of our marketing blogs, repeated last autumn, we advised selling the sizzle, not the sausage. In other words, we recommended not trying to describe your book to the reader but trying to excite their imagination about how dramatic/entertaining/insightful/hilarious (insert other adjectives of your choice) your book is going to be. That is exactly what this book strives to do. That was good enough to convince me to buy the book. If it does that for us, the money spent on it will be repaid just by selling two extra copies of one of our books. As both an author and a publisher I have written dozens of book blurbs, so I thought I knew what I was doing. We had done plenty of research to try to find out what made a good blurb and we followed the lessons we had learnt, but there was still a nagging doubt in our minds that we might not be getting it right. Our sales suggested that there was something amiss. We were getting lots of clicks on our adverts, but they weren’t converting into as many sales as they should.  So, when I started to read this book, pennies started to drop to tell me that doing what other people were doing was the problem. What we needed to do was to be different, to make our blurbs stand out from the crowd. Readers are too easily distracted by metaphorical shiny things, so the solution to that is for our book blurbs to be the shiny thing that distracts them from other books. Chapter by chapter, Phoebe (if she’ll permit me the liberty of addressing her by her first name) lays out the elements that go into writing the “killer” book blurb that we wanted, and then how to structure the different elements to get the most out of them. It wasn’t that the blurbs we wrote were actually bad. After all, we're conforming to what we understood to be “best practice”. It was more that they could have been so much better. For the most part, they were selling the sausage, not the sizzle. They described the book, but they didn’t describe the emotional ride that was contained within the book. Emotions, it turns out, are the sizzle that sells the sausage.  I sort of knew that already, because I have always believed that books should be character led, not plot led. Readers engage with the characters at an emotional level and come to care about them and that is what keeps them turning the page, not the plot itself. And that emotional engagement, it turns out, is what has to be at the heart of the book’s blurb. There is a lot more to it than that of course. Conflict, jeopardy, structure and vocabulary all play a massive part, but without the emotion the book still won’t sell. I’m not going to ruin the book’s sales by telling you what tools and techniques are taught within its covers. You’re going to have to pay to find out, just as we did. Suffice to say that every page provides something new to learn. Even if your blurbs are already good I feel quite confident saying that you will learn something new from this book. Readers will note that I have given the book only 4 stars where, from what I have said, you might expect that it should be worth five stars. That isn’t because of the lessons that the book teaches. It is only because of the style in which those lessons are taught. "As an author and as a publisher I have limited time available" The author uses well known books and films to illustrate the lessons and there is nothing wrong with that. Many of those books and films are her personal favourites. Again, there’s nothing wrong with that. However, at times I found that the point being made was laboured and that the author was getting rather carried away with her own passions. While such enthusiasm is to be admired, it can be a little too much when the reader has already grasped the key message and only wants to move on to the next lesson. As an author and as a publisher I have limited time available, and this book took a little more time to read than was essential. Perhaps it was designed to pad the word count, so the reader thinks they’re getting value for money, but the real value isn’t in the number of words, it’s in the messages. But that is a minor criticism and I feel secure in saying that anyone buying this book will have their money repaid quite swiftly if they learn the lessons and apply them to their blurb writing.  So, what are my main takeaways from this book? The first one I sort of already knew but being reminded of it didn’t hurt. The purpose of the blurb is not to describe the book; it is to sell the book, which is an entirely different technique. According to Phoebe, you don’t even have to read the book to be able to write its blurb. Secondly, creating a good blurb isn’t easy and it requires practice and hard work. I soon discovered that when I tried to re-write the blurbs for the books we publish. What I thought would be about ten minutes work per book turned out to take considerably longer and they still aren’t perfect (though they are better). Finally, a good blurb taps into your emotions and raises the “risk” level for the protagonist so high that the reader has no choice but to buy the book to find out what happens. Get that right and the book will sell. But I’m sure you want to know if re-writing the blurbs for our books made any difference to our sales.  First of all, judge for yourself. If you go to our “Books” page we have re-written most of our blurbs. I’m not suggesting they are perfect. In fact, I’m sure that Phoebe J Ravencraft would suggest some improvements if she were to read them. But they are different to our previous style. Just ask yourself one simple question – having read any of those, do you feel tempted to buy the book? More importantly, has our conversion rate for sales improved? We actually got an instant return for one book. The day we changed the blurb it got its first sale in months. Coincidence? Possibly, but we think it may have been the new blurb. Then a second book got its first sale in months, followed by a third. Too many for coincidence; this was a trend. I’m not going to pretend any of those books went from non-seller to best-seller overnight as a result of the tweaks we made - but “Fiction Blurbs: The Best Book Forward Way” paid for itself within a week and is still paying for itself in terms of sales. I highly recommend “Fiction Blurbs The Best Book Forward Way” by Bryan Cohen and Phoebe J Ravencraft. To find out more about the book, click here. Next week we’ll be reviewing another book which could help you to sell a lot more of your own books, so be sure not to miss our blog. In fact, why not sign up to our newsletter to make sure you don’t miss it. We’ll even send you a free ebook if you do. Just click the button below.  In last week’s blog we asserted that understanding a protagonist’s motivation was one of the critical factors in creating interesting characters for stories. In fact, we went further than that and said authors should be doing the same for antagonists as well. But in order to do that we also need to understand how and why motivation works in general otherwise we can’t attribute the right motivators for the correct reasons. For example, if our story involves a love triangle, what might motivate one of the characters to abandon their love in order to make the object of their love happy? In a selfish world like ours that makes no sense. But it is a well-used trope in romance. Which is what this week’s blog is about. It’s a whistle stop tour of motivational theory and what it can do for you as an author.  Motivation or Incentive? Motivation or Incentive? The first thing to understand is that there is a significant difference between motivation and incentive. The big difference between the two is that an incentive can never be enough for a person to place themselves in jeopardy. After all, there’s no point in being paid £1 million (an incentive) if you are going to end up dead and can’t spend it. But a person may take a dangerous, high paying job if it is the only way to provide security for the ones they love. Love is a motivation, money is an incentive. To put it another way, motivation drives us, but incentives can only pull us. In fiction we are always looking for what drives the character. The lure of wealth may be an incentive for a criminal, but it carries the risk of imprisonment. So, what motivates criminals to take that risk? Understanding that motivation makes the criminal far more interesting than just the lure of wealth, which is quite shallow.  Psychologist Abraham Maslow, the granddaddy of content based motivational theory. Psychologist Abraham Maslow, the granddaddy of content based motivational theory. Theories of motivation are generally grouped under one of two headings: content and process. Content theories focus on what things provide motivation and process theories focus on how motivation occurs. To add depth to a character it isn’t enough to know what motivates them (content) it is also important to know why (process). The two together provide layers of complexity and that makes characters more interesting. Abraham Maslow is the granddaddy of content theory. He theorised that in order to function at a higher level, you first required certain needs to be satisfied. In other words, you can’t create great art if you are starving to death. So, you have to have your hunger satisfied before you can achieve your goal to become an artist. This became known as a “hierarchy of needs”. 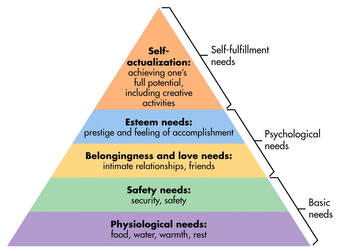 Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Maslow's hierarchy of needs. You may, at this point, be tempted to mention the name of Vincent Van Gogh, who only sold one of his paintings during his lifetime. But he wasn’t actually poor. He had a very well paid job selling art in his brother’s Paris gallery before he left to pursue his own artistic career. Van Gogh wasn’t penniless at the start of his career – though he may have been by the end. In practice this means that we are first motivated by a need to survive, but if that is secure we can then move on to be motivated by something at a higher level. In fiction this means that if a character is trapped inside a burning building, they aren’t going to be interested in catching the person that lit the match. Only after they have escaped the inferno will they turn their attention to that. A vagrant living on the street wouldn’t be motivated enough to help a damsel in distress, because their priority would be their own survival. But they can be incentivised to help the damsel because the incentive (usually money) secures their basic needs. However, if it looks like they may die in the attempt, the incentive would no longer be enough. They would need some other motive, such as love for the damsel. While good Samaritans may exist, they don’t place themselves in danger. They need motivation for that to happen.  GET MOTIVATED! GET MOTIVATED! As can be seen from that example, content based motivation is a tricky business and if you don’t understand those sorts of basics, your readers won’t believe in your characters. But notice the sorts of things that appear in Maslow's hierarchy of needs diagram from the third level upwards. there's plenty of stuff hidden behind those short statements with which you can play in order to provide your characters with motivation. But what content theory also makes clear is that what motivates us isn’t constant. Our motivation can change in response to circumstances. For example, we may be highly motivated to succeed in our careers, working long hours and totally immersing ourselves in our jobs. Then one day we meet the girl (or boy) of our dreams and suddenly our career isn’t the most important thing in our lives anymore. Winning the heart of the object of our desire is now what is uppermost in our minds, to the extent that we may throw away our career in order to be with that person. That, of course, runs contrary to Maslow’s theory, because if we lose our job we also lose our security. So, it appears that some motivators are more powerful than others, at least for some of the time.  Achievement and competition. Achievement and competition. Achievement and competition are theories of content motivation studied by David Mclelland. Today this is often portrayed in fiction as a negative thing; highly motivated achievers or competitors are often depicted as criminals or cheats, driven by their desire to win at all costs. Which is odd, because the sports stars we admire the most are highly motivated by competition and achievement. Not only do they compete in their sporting arena, they also compete off the field by consistently trying to beat their own best performances, in the gym for example. Name the sports star you admire the most and you are naming a highly motivated competitor, but modern fiction suggests you will also be naming a cheat. I think we need to change that stereotype with positive competitive role models in fiction. Is competition and high achievement a bad thing? That is for you to decide, but I know of one author who uses competition as a motivator for the success of his heroic characters.  Psychologist B F Skinner Psychologist B F Skinner When it comes to process theories, there is one that is usable in fiction. It is “reinforcement” theory, developed by B F Skinner. This is based on positive outcomes of certain types of behaviour. In fact this can be traced back even further, to Pavlov and his dogs, but Skinner is better known for his study of humans. If you can imagine a misbehaving child being given a biscuit in exchange for better behaviour, it will soon learn that if it misbehaves biscuits will be forthcoming, so that the reward becomes the motivator for bad behaviour. Extending that theory into adulthood, if a character believes that rewards come from bad behaviour they will continue to behave badly – which is great motivation for criminal characters. The opposite applies as well, of course. If good behaviour results in good outcomes, then a character is motivated towards good behaviour. It may also surprise them when their good behaviour results in a bad outcome, eg their loyalty being betrayed. That could be enough for a previously good person to start behaving badly. Because when we add emotions to motivation, we start to get a powerful mix. I have already mentioned the power of love to derail a career, but there are plenty of other emotions that can affect motivation. The most challenging question it is ever possible for an author to ask is what makes one man brave and another a coward. This is especially so in stories that involve death but can also be played out in terms of moral behaviour. Nature has given us three responses to danger: fight, flight or freeze. What makes one person choose to fight, another choose to flee and another to do neither (freeze)? Fear is a natural response to danger, so all three responses should be regarded as equal, because nature gave us the choice. But our regard for bravery and our contempt for cowardice shows that we don’t regard all three responses as being equal. Very often the individuals who take the actions can’t answer our question. Ask most decorated war heroes why they did what they did, and they are unable to answer, or they fall back on clichés like “duty”.  But duty only takes us so far. A soldier standing firm in the line of battle is doing his duty. A soldier that charges an enemy position in order to save a comrade is going far beyond that. It happens in real life, but quite rarely which is why medals such as the Victoria Cross and the Congressional Medal of Honour exist to recognise such actions. But in fiction it is the norm for the protagonist to exhibit that level of bravery and persistence. So, what can we give them, in emotional terms, so that they do that? And, more importantly, how can we create a backstory that shows how they developed that quality, based on what we know about motivation? This is where Skinner’s theory becomes important. If during their developmental years the character is rewarded for having beliefs and values that we admire, but isn’t rewarded for having beliefs that we detest, the qualities for which they were rewarded will become the motivators. They will also become the barriers when those qualities are undermined. The flawed protagonist is one whose beliefs and values are called into doubt by events, which cause them to question their beliefs and results in internal conflicts. The loner cop who drinks way too much whisky didn't start out that way. Something made them like that and the author gets to decide what it was. There is far more to motivation than I have had time to cover in this blog. I recommend further research. How much you include in a story is up to you, but layered characters with strong motivations are always going to be of more interest to readers than shallow characters who only respond to incentives. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so.  As publishers, we get sent a lot of books. But that’s OK because we’d be in trouble if people didn’t send us their books. It would be nice if I could say that all those books are great, and we can’t wait to be able to get them uploaded and out there with the reading public. Unfortunately, we can’t say that. I would estimate that perhaps 50% of what we are sent is never going to get published; not by us and not by any other reputable publisher, large or small. It usually takes us less than an hour of reading to make that decision. About half the rest start off well but then start to run out of steam, usually around the 30 to 40,000 word point. It was probably around that point that the author realised that writing a book wasn’t quite as easy as they had thought, but they kept ploughing on anyway, in the hope that something great would come out of it. Sadly, it didn’t, but it will take us maybe 2 – 3 hours to decide to pass on those books.  Finally, we get to the 20% to 30% of books that stand a real chance of finding readers. Those are the ones where we invite the author to work with us to try to get the book into its best possible version before we finally publish it. Some authors then pass, because they think their book is good enough already and doesn’t require our interference, or maybe they think they can get a better deal elsewhere (and maybe they can). But if a book is on our website it’s because the author has been more realistic and understands that all work can be improved, even if it is only a little bit. Just once in a while we get a book sent to us that we know from page 1 is going to be good. How do we know that? Because we get so absorbed in it that someone has to tap us on the shoulder and remind us that it’s time to pack up work for the day. Even then we’ll upload it onto a tablet so we can keep on reading it on the way home (but not if we’re driving). "Character = Conflict = Plot" Those books may be rare, but when we analyse what they have that other books don’t have, it usually comes down to just 3 things.
You will notice that I haven’t mentioned the plot. That’s because the plot is not the main driver of our engagement with the story. The protagonist and the problem(s) they face are what hooked us: character + conflict = plot. You will also notice that I mentioned the antagonist as being one of the 3 things that hooked us. Antagonists don’t get many mentions in blogs about writing and that’s a shame, because without an antagonist you only have half a story. Where would James Bond be without Goldfinger or Blofeld? Unemployed, that’s where. It is our contention (feel free to disagree) that a well-constructed antagonist is as important to a story as a well-constructed protagonist. For every Snow White, we need a Wicked Queen.  Think of Darth Vader. He starts off as the archetypal antagonist, just bad because he’s bad. But then we find out that he is Luke Skywalker’s father and, all of a sudden, he becomes much more interesting. He becomes so interesting that a considerable proportion of the next 3 Star Wars films are devoted to his “origin” story (Ep I: The Phantom Menace, Ep II: Attack of the Clones and Ep III: Revenge of the Sith). Yet time and again we get books submitted to us with antagonists so one dimensional we feel no emotional interest in them. We need to despise the antagonist in order to make it more important for the protagonist to succeed. But in those stories it is often like trying to despise Wiley Coyote or Elmer Fudd. But I’m getting ahead of myself. Number one in my list was the protagonist.  So, what makes a good protagonist? That will vary from genre to genre. For fantasy fiction they are required to be heroic, while for romance the first requirement is that they be attractive in some way (it doesn’t have to be a physical attractiveness). But that is just the surface level. The more complex the character, the more interesting they are. The more interesting they are, the more interest the reader will take in them. And the more interest the reader takes in them, the more likely it is that they will continue reading the book. It is very important that readers continue to read the book. If you are an Indie author, you need those readers to post favourable reviews of your book in order to sell more copies. And if you want to find a publisher, you have to submit a book that the publisher wants to finish reading.  Building complexity into a character, however, isn’t simple. It takes time and it takes an understanding of people. There are a few short cuts that can be taken, tropes as they are known, such as giving them secrets, but the thing that really catches the imagination is their motivation. Why are they doing what they are doing? After all, they could just as easily stay at home with their feet up reading a good book, like the rest of us. The reader has to believe that the protagonist is dealing with the conflict because they have a really strong reason to do so. But that leaves the reader with a gigantic “why” to be answered. And the only person who can answer it is the author.  Take Jack Reacher, for example. He is a drifter, a loner, and he doesn’t have to get involved in the problems of others. Yet he always does. He is motivated to help by a range of different things, depending on the plotlines, but the one that recurs most regularly is the desire to fight injustice in whatever form it appears. It may be the injustice of a small business owner having to pay protection money to gangsters, or it may be the injustice of the law not taking a victim seriously. It may be the injustice of the police being too incompetent to find the real criminals. It may even be the injustice of someone being wrongly accused of a crime. But whatever it is, it motivates Reacher to get involved when he really doesn’t have to. So, what motivates your protagonist to get involved when they don’t have to? And why does that motivate them so much?  Internal conflict is always good for adding layers of interest to a protagonist. That can be introduced in many different ways, from a lack of self-belief to questions about the morality of what they are doing. It is especially useful when internal conflicts start to impact on whatever goal the character is pursuing. Think about a vegan being attracted to someone who works in an abattoir – can you imagine the complexity of making that relationship work? It doesn’t always have to be as blunt as that example. In fact, subtlety often makes it more interesting, especially if the internal conflict is revealed slowly over the whole book rather than in one big lump, so that the reader says “Ah, now I see what the real problem has been all along”. To really get to grips with both motivation and internal conflict you have to research your character(s). Yes, I know you only just created them, but that doesn’t stop you doing “research” on them. All you have to do is ask the right questions – then answer them.  Dress your characters. Dress your characters. Start with their parents: were they loving, cruel, dismissive, encouraging or even absent? Parents are the first influence on a child and therefore the first to influence your character’s personality when they are older. From there you can move onto teachers, peer groups, young adulthood and the dreams and aspirations that come with it. For older characters, the age of Jack Reacher for example, you may want to continue that research into their 20s and even 30s. You dress your characters with their life experiences, their beliefs and their values the same way as you dress them in their clothes, and those things then provide their motivation and/or internal conflicts. If they fight injustice, then what is the injustice they suffered that makes them want to do that? If they are on a quest, what is it they are seeking to find out about themselves along the way? If they are afraid of starting a romantic relationship, what happened in their past that makes them so afraid now? I’m not going to ask all the possible questions; you are the author, they are your characters, you need to ask the questions. But the better the questions you ask, the better your characters will be.  And the same applies to antagonists. We are familiar with the surface level motives of antagonists: love, hate, jealousy, greed, lust for power, revenge, etc. But no one is born seeking revenge. No one is born jealous. No one is born lusting for power. So, what was it in their life that changed them and gave them those surface level motivations? What happened to make a “normal” human being want to rule the world?  You can throw in psychological motivations, such as psychopathy, sociopathy, narcissism megalomania, paranoia etc but even they require some sort of explanation. If you are going to use them you will need a good grounding in psychology and/or mental health so that you can understand what your antagonist’s backstory has to look like in order for them to suffer from those forms of psychological disorder. If you can come up with two complex characters (protagonist and antagonist), you are going to come up with a complex, layered conflict between them that holds the reader’s attention and has them crying out for more. And if you can come up with those 3 elements, you are going to find a publisher who wants to publish your book. If you have enjoyed this blog, or found it informative, then make sure you don’t miss future editions. Just click on the button below to sign up for our newsletter. We’ll even send you a free ebook for doing so. Disclaimer: We are not connected to Book Brush in any way other than as users of the product that has been reviewed. This review has not been paid for by Book Brush or by any other person or organisation.  This article is a review of the Book Brush app which allows authors to design their own book covers, rather than having to pay someone else a lot of money to do that for them. I have to say up front that some of the things that Book Brush allows you to do can be done just as easily in PowerPoint (if you are good at using PowerPoint) but, equally, some of the features are unique. And what is most unique as that it draws together everything you may need to be able to do under one URL. The service is provided on an annual subscription basis, charging at 3 levels: silver, gold and platinum. We paid for the silver level ($99, about £85) as that provided the things we needed right there and then (we knew we could upgrade later if we wanted to). Looking at the other two packages, it is hard to see them offering that much more – but on the other hand if it is something you want to do repetitively and you have no other way of doing it, you may regard the extra money as being well spent. I’ll cover the differences in the subscription levels a little later in this blog. "doing it myself was a no-brainer" The first thing I found useful was the introduction video that showed me how to use the app. I was able to watch it before I had even subscribed, and it persuaded me that what was on offer was going to save me money. Typically, we pay a designer on fiverr.com around $100 to provide us with an ebook and paperback cover package (with us providing the images to be used) and, as publishers, we may need a dozen of those each year, costing around $1,200. So, paying $99 a year and getting one of our team to do it was a no-brainer, providing we can create the sorts of designs that we want. How long does it take to design a cover?  Having watched the video and learnt the basics, and combining it with some use of PowerPoint (I’ll tell you why later) I was able to create a cover for the next Carter’s Commandos book in around 15 minutes. OK, the design isn’t complicated, but using the sorts of templates that are available within Book Brush, it wouldn’t have taken much longer to produce something more elaborate. I was able to do that after watching just one video and spending about an hour playing around with the various features. What’s more, I rather enjoyed doing it because the results are so easy and quick to see and it’s fun to be able to experiment with different designs. Warning to procrastinators: It is very easy to spend a lot of time playing with Book Brush while convincing yourself you are doing something productive. So keep an eye out and don't fall into that trap when you should really be writing. At the end of the process we know that by using Book Brush templates, our finished cover is going to be fully compatible with the technical requirements for KDP and other book publishing sites. But the biggest advantage is the range of templates that are available and how you can manipulate them to create a design that is unique to your book. The templates and other images are conveniently organised into genre specific groups.  KDP cover creator offers you about a dozen templates and they are pretty much fixed. You can add your own images, of course, but trimming them is difficult and it is inevitable that your book cover is going to look like hundreds of others, which is where Book Brush offers one of its great advantages. Not only that, but you have an almost unlimited ability to change colours and fonts. The platinum subscription for Book Brush offers the flexibility to remove backgrounds from images, but you may not want to pay for that. Removing background allows several images to be combined to create unique covers. Which is where PowerPoint comes in. If you know how to do it, you can remove backgrounds from images in PowerPoint, save the combined image as a .jpg and then import it into Book Brush ready to use. I’m not going to go into detail about how to do that in this blog. We searched YouTube and found this “how to” video for people who don’t already know. Along with all the templates Book Brush also has access to hundreds of thousands of free to use images which you can apply to your covers but, of course, you can also create or buy your own. They have a wide range of fonts and all the special affects you would expect to see for applying shadow, changing transparency etc. If you want to use a particular font and it isn't available in Book brush, you can import it.  There are also some blogs on the site that could be helpful to you, such as the one we read to discover what fonts work best for which genres and which should be paired together to differentiate between titles, sub-titles and author names. So, what more do you get if you upgrade? With the gold package you get templates into which you can insert your finished covers in suitable formats to use for your social media marketing, cover reveals etc, such as showing the cover in a Kindle frame with accompanying promotional text. That was about all I saw there that was different and not something that I considered to be worth paying for. With platinum you get the ability to create video trailers for your books, by combining either your own video images or using their collection of stock video. To that you can add music or a narration. The package is quite easy to use, can create videos compatible with the different social media platforms and the results look very professional. But it isn’t something we would use a lot so, in our opinion, it didn’t justify the additional $147 subscription fee.  If they offered the opportunity to buy a one-off video package for $10 - $15, we’d certainly use it, but I don’t think the subscription offers value for money unless you’re going to be creating a lot of video trailers. Where Book Brush really comes into its own is in creating paperback and hardback covers. With the wide range of trim sizes on offer through KDP and the wide variation of page counts between books, coming up with a PowerPoint template that works for every book is impossible, so it’s all down to trial and error, which can take hours of work to get right. But Book Brush just asks you how many pages your book has and then creates a custom template for you which is guaranteed to pass KDP’s quality standards. All you have to do is overlay the different content you want to use for your design and, again, you can use their designs and images or create your own. So, overall we are quite happy with Book Brush. It’s easy and quick to learn and you can start producing professional looking book covers within an hour of paying your subscription. We certainly recommend the silver package. Whether you want to pay more for the extra buzzers and bells is down to you. If you would like to know more about Book Brush, click/tap here. If you have enjoyed this blog or found it informative, be sure not miss future editions by signing up for our newsletter. We’ll even give you a free ebook for doing it. Just click the button below. It's New Year and we here at Selfishgenie Publishing are taking a well earned break.
But don't worry, our blog will be returning on Saturday 7th January 2023, so watch our socials for information on what we will be blogging about. In the meantime, we would like to wish you a very Happy 2023. And don't forget, books published by Selfishgenie are a great way to use those Amazon vouchers you got for Christmas. |
AuthorThis blog is compiled and curated by the Selfishgenie publishing team. Archives
March 2025
|
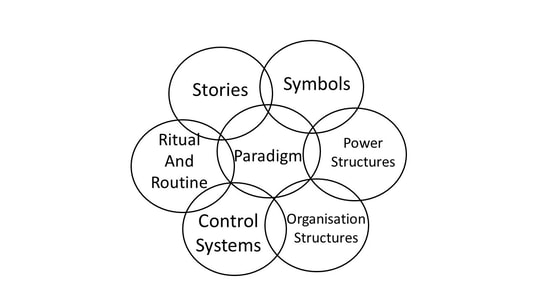




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed